Proxy and Reverse Proxy every DevOps novice must know
You must have heard this term around often in the day to day work but especially in the college days where students generally mark the attendance proxies for their buddies. (Good old days ;) )
Now that we have got over the nostalgia; we can go over to understand this concept in brief.
Consider a Scenario where John wants to send a message to Julie but he cant directly send it to her as her parents are strict and do not want any boy to meet her. But her friend Samantha comes to your rescue as she is well acquainted with you so she is the one who channelise the conversation between John and Julie.
I will try to link the above situation with the core concept here.
Ever faced situations like
Cant access the site from the office / educational institute because it is blocked ?
Cant access some site because you dont have the access to the network outside ?
You want to access some YouTube video which is not available in your country ?
Ever tried to solve some above problem yourself. If you are that D.I.Y. guy you must have tried some application called as "proxy".
Proxy is something in this case which bypasses all these restrictions and get you the content you wanted.
So to connect the dots here from the above example
John here acts as your "Browser"
Samantha here acts as your "Proxy"
Julie here acts as your "Website you want to access from the Browser"
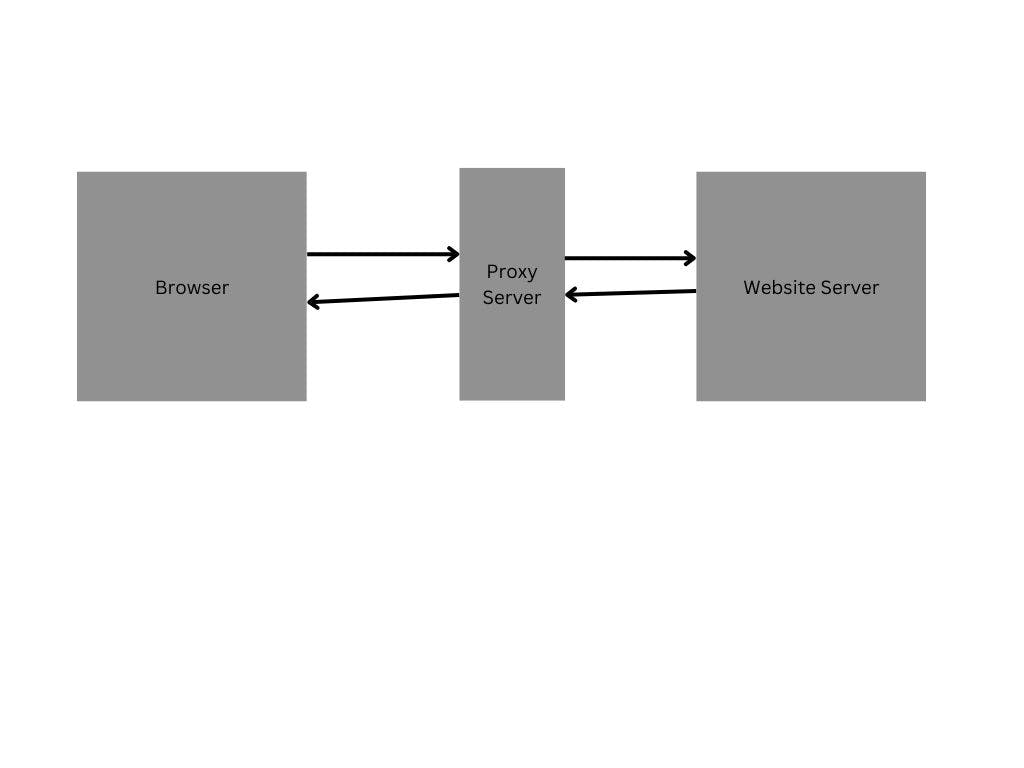
So here the Proxy Server acts as the intermediary between the Browser and the Website Server (aka Origin Server).
Generally, when you browse a site or a service, your PC/device send request to the origin server which hosts the site/service and send you back the content you wanted.
But in terms of proxy we send the request to the ‘proxy server’, it gets your request which let it know which server you wanted to contact, then it makes the request to the Website Server (Origin Server), get the content and send it back to you.
Generally the proxies are mainly divided into two types
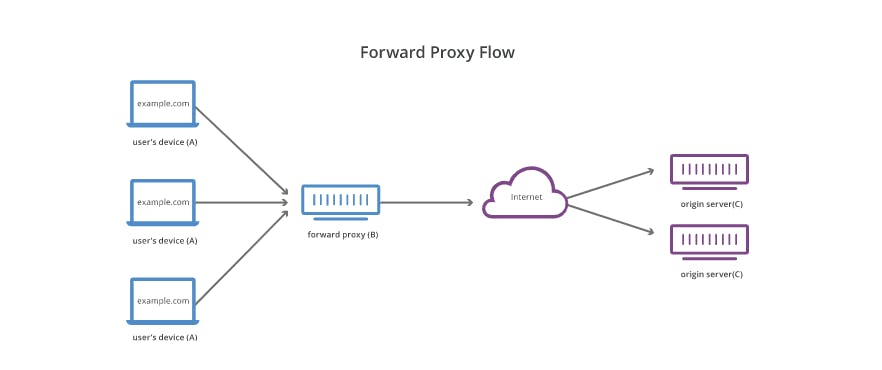
1. Forward Proxy Servers
A proxy server is a system or router that provides a gateway between users and the internet. Therefore, it helps prevent cyber attackers from entering a private network. It is a server, referred to as an “intermediary” because it goes between end-users and the web pages they visit online.
When a computer connects to the internet, it uses an IP address. This is similar to your home’s street address, telling incoming data where to go and marking outgoing data with a return address for other devices to authenticate. A proxy server is essentially a computer on the internet that has an IP address of its own.
The Benefits of the Forward Proxies
Anonymous Browsing: Anonymous proxies allow users to browse the web anonymously by concealing their IP addresses.
Security: Some proxy server types (e.g., HTTPS proxies) can be configured to provide secure connections through encryption.
Web filtering: Organisations often use transparent proxies to restrict employees from accessing certain websites. Transparent proxies also log user activity, allowing organisations to monitor employees' Internet use at work.
Changing Geo-Location: Organisations can use rotating proxies for Internet-based marketing activities where data is dependent on geo-location. Such activities could include price aggregation, web scraping, market research, and SEO.
The Disadvantages of the Forward Proxies
Lack of encryption: Unless a proxy is configured with encryption, it will operate through an unsecured connection. Attackers can easily intercept communications over unsecured proxies, meaning any sensitive data like usernames and passwords are at risk of being compromised.
Data logging: Proxy servers store users' IP addresses along with their web request data. Some proxies do not encrypt this information and, depending on the service, may even sell the data to other parties.
Inconsistent speed: Free proxies are susceptible to traffic overload. Servers often do not have the necessary bandwidth to serve thousands of users at once with maintained speeds and are prone to lagging.
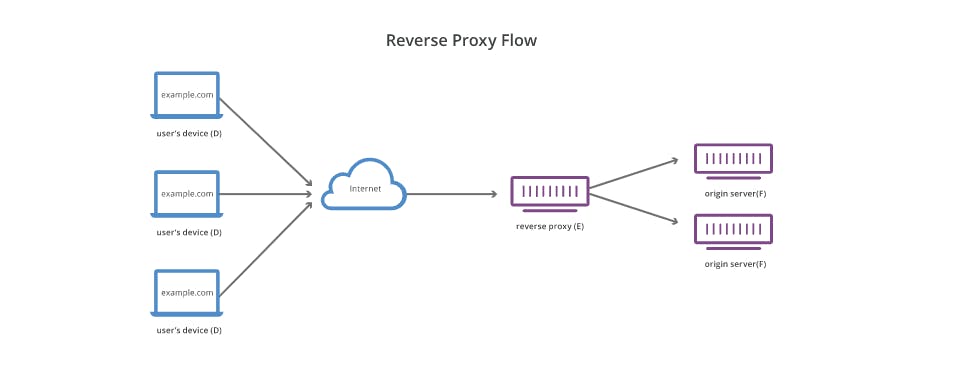
2. Reverse Proxy Servers
The reverse proxy sits in between the one or more servers and intercepts the request from clients. The key difference between the forward proxy and the reverse proxy is that the proxy sits in front of the client whereas the reverse proxy when clients send requests to the origin server of a website, those requests are intercepted at the network edge by the reverse proxy server. The reverse proxy server will then send requests to and receive responses from the origin server.
The Benefits of the Reverse Proxies
- Load balancing
- Protection from Attacks (Privacy)
- Caching
- SSL Encryption
The Disadvantages of the Reverse Proxies
Reverse proxies require additional network resources and processing power in order to operate. Resources must also be distributed between public and private ports when deploying virtual hosting, resulting in additional hardware requirements.
A lack of visibility into client requests and content passing through the reverse proxy server makes troubleshooting difficult during production deployments.
Reverse proxies can add latency to transactions and limit performance by limiting options for load balancing and content delivery.
The Subtle DIFFERENCE
Forward Proxy sits in front of a client and ensures taht no origin server ever communicates directly with the client
Reverse Proxy sits in front of the origin server and ensures that no origin server ever communicates directly with that origin server.
# Application for the Proxies
Proxies may be used by individuals for personal uses such as masking their location. When implemented by organisations, they can be set up to:
Enhance security
Increase privacy of employee’s internet browsing
Balance internet traffic to prevent computer program failure
Manage site access for employees in the working environment
Reduce bandwidth (maximum rate of data transfer over a given path) by caching files or compressing traffic.
Other Types Proxies include:
- Bypassing filters
Proxies allow users to own an IP address with a different location. This is how users can access and bypass restrictions imposed by some websites.
- Logging and spying
Proxies hide the original IP address of the user. It makes the requests appear like it came from a completely different source.
- Email Marketing
Proxies are your virtual best friends that allow your business to send emails, which is a major part of any company’s email marketing campaign. Companies receive a lot of emails from prospects, including emails from random senders, which might contain malicious URLs.
But with the help of proxy servers, you can do email marketing in a safe and secure manner without any worries of email sabotage. Wondering how? Well, proxy servers can help you detect emails with suspicious URLs, which will protect your data
Improving performance (with a caching proxy)
Geo-targeted advertising (by advertisers)
QUICK F.A.Q's
Q. Is a VPN the Same as a Proxy Server ?
NO, VPN route all internet traffic through an encryption tunnel, but Proxy servers only operate with single apps or websites.
Q. What is a Proxy Server Used For ?
Proxy servers are primarily used for cybersecurity purposes. Because they sit between users and the internet, proxy servers can stop cyber criminals from connecting to a private network.

